
Key Challenges and Solutions in Building Scalable SaaS Applications
In today’s increasingly dynamic digital era, Software as a Service (SaaS) applications are the lifeline of many businesses. Such applications, therefore, become lifelines for most businesses, delivering the very best comparison for efficacy from automating workflows to enabling workforces for multinational collaboration. In a growing business and demanding operations, scaling these applications is critical, too, without increasing performance worries. Scalability then becomes an imperative, most probably the ability of a system to support larger workloads without sacrificing functionality.
The scalability of SaaS applications is, therefore, not a matter of plugging additional servers or having more storage attached. It is about conceptual robustness, geo-resilient systems, and futuristic blueprints in design. This article throws light on the major challenges that developers face in the scalability of SaaS applications, how to best navigate those challenges, and how monitoring, maintenance, and new trends will shape the future of SaaS scalability. It doesn’t matter whether you are developing a brand-new SaaS product or enhancing an existing one, but knowing all these areas ensures success for many years ahead.
Scalability in SaaS Applications: What You Should Know
The growth of its population of users, sizes of data, workloads, and so on are the main considerations from the viewpoint of SaaS development cost and scale today. The meaning of scalable, in other words, applied to a SaaS application, denotes the ability of the software to uphold functionality, reliability, and usability, regardless of the actual demand to scale up. The scalability, therefore, for the SaaS, making it a viable feature, will eventually convert into customer satisfaction and possibly future revenue growth for those companies.
So, what makes SaaS scaling unique? Here are a few clarifications:
- Vertical scaling: Upgrading existing workhorse infrastructure, i.e., upgrading servers or enhancing databases.
- Horizontal scaling: Increasing the system by adding nodes or servers such that the workload is evenly distributed across them.
- Elastic scaling: A more dynamic resource scaling as per demand; systems scale up in high hours of use and scale down in low hours of use.
For SaaS developers, knowing these dimensions is critical for designing systems that grow unpredictably. Scalable applications cater to current user requirements while predicting future demand, and thus, scaling is a pillar of continued success. Whether it’s enabling millions of concurrent users or integrating with outside platforms, scalability ensures that the SaaS holds its ground in an ever-changing competitive market.
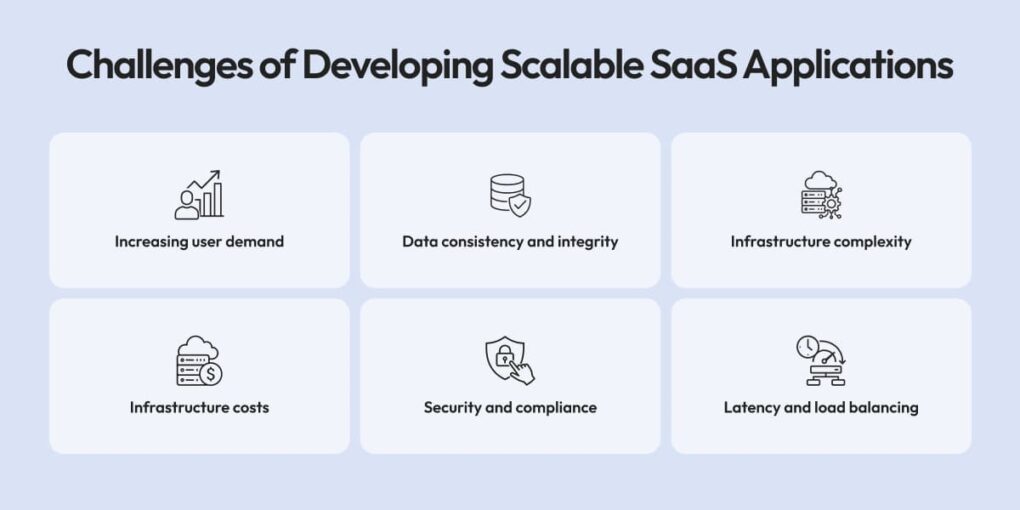
The Challenges of Developing Scalable SaaS Applications
The technical and operational roadblocks in developing scalable SaaS applications are often significant. These challenges can emerge at nearly every stage of the development lifecycle and directly affect performance and user experience. In SaaS application development, scalability issues usually become visible only when real user growth begins, which is why they require early architectural planning. Leading SaaS development companies like Cleveroad, that work on complex SaaS platforms, often highlight the following challenges as the most common:
- Increasing user demand support: More users imply that the systems must support traffic and data loads seamlessly. Unfit systems lead to poor performance, resulting in sluggishness and even crashes.
- Data consistency and integrity: Maintaining data consistency is challenging in a scalable SaaS system, particularly with horizontal scaling.
- Infrastructure complexity and costs: Infrastructure complexity with increased application scale. Horizontal scalability through additional servers is easy; it is resource management that produces the hassle and increased expense to manage it.
- Security and compliance: Security should never be traded off for scalability. Protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance with industry requirements and regulations becomes more difficult as applications scale.
- Latency and load balancing: An important challenge to overcome is scaling workloads across servers so that it is efficient for high loads and low latency. Load balancing ensures a single server is not being overloaded, but it is hard to achieve when scaling a particular infrastructure.
Solutions to Scale SaaS
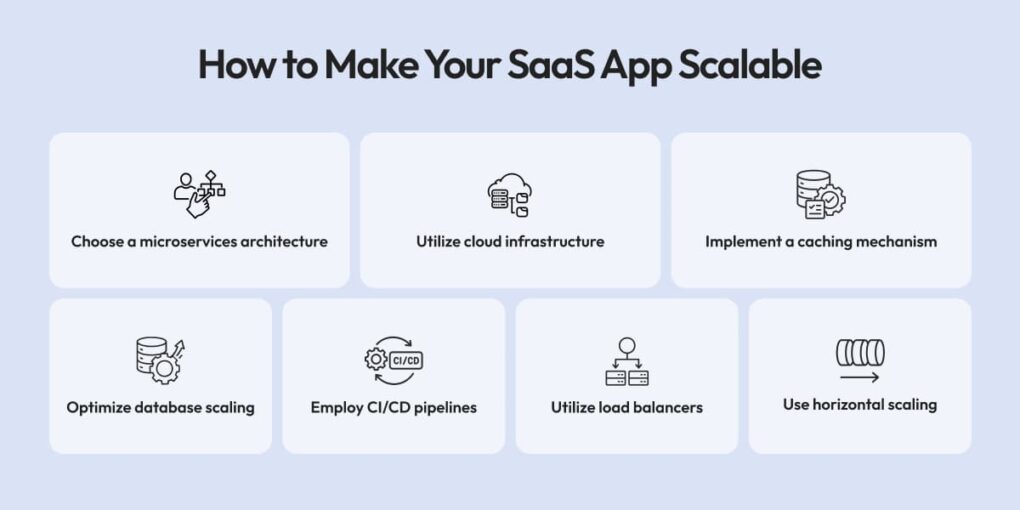
Scalability solutions for a SaaS application often involve strategies, technologies, and best practices, among others. A proactive consideration of scalability challenges by developers, rather than waiting until applications need to grow with increasing user demand, would ensure that applications perform well and are highly reliable and secure. The following explains the correct solutions to scaling a SaaS application:
- Choose a microservices architecture: Microservices are one of the greatest possible options for scaling SaaS applications because microservices decompose any application into microservices, little independent services that scale independently by allowing individual components to grow just when they want, with little or no impact on the rest of the application.
- Use horizontal scaling: It entails adding more servers or more instances when needed to increase capacity against increased demand. In this scenario, cloud platforms allow for the allocation of that resource based on actual demand, allowing the possibility for SaaS platforms to absorb the shock of traffic without being penalized in performance.
- Utilize cloud infrastructure and platforms: With big names in the sector like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, any type of vertical and horizontal resource scalability is possible. In fact, things like auto-scaling, load balancing, and storage management typically do the job without worrying about the complexity of on-premise infrastructure.
- Implementation of caching mechanism: Caffeine is a powerful method of reducing database stress and thus optimizing performance for applications by allowing frequent access to data in memory. Such an increased speed of response and reaction enables applications to service more concurrent transactions without hindering back-end resources. Redis and Memcached are some popular choices for caching.
- Optimize database scaling: In layman’s terms, bottlenecks for most databases scale with the size of data. Some interesting techniques in solving this problem include sharding and replication. Sharding has the meaning of breaking databases into separate servers, while replication essentially means adding the same data to all nodes.
- Automated testing and continuous integration: The greater the scaling, the more complex the code becomes as far as keeping proper code quality goes. Automated testing and Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines incorporate changes so that the new features added can be tested often and integrated seamlessly, thus ensuring no performance issue is introduced.
- Utilize load balancers: Load balancing means distributing incoming traffic flow across multiple servers so that no individual gets overburdened and stressed. Load balancing is paramount when traffic is high, uptime and maintenance, and user experience excellence on-site.
The Importance of Monitoring and Maintenance in SaaS Scalability
With time, SaaS applications go up, and it is really important to keep monitoring and maintaining all aspects in order to ensure their scalability with reliability and a safety net. On the demanding and ever-growing list of users for SaaS applications, there is no alternative to continuous monitoring and maintenance that can proactively assist in identifying bottlenecks and prevent the possibility of performance issues while also allowing the application to be scalable without disruptions. Here is how monitoring and maintenance help scalability:
- Real-time monitoring for proactive resolution of problems: Continuous monitoring helps in the identification of potential issues before they affect users. For example, tracking some key signals such as server load, database performance, and application response times all come in handy in quickly detecting anomalies and giving way to solving the issues through application performance monitoring (APM) software, server monitoring, and log aggregation.
- Optimization of system performance: As applications scale, they can even deteriorate and suffer from a lack of regular maintenance. Regular checks usually identify lazy database queries, overworked servers, cost-inefficient codes, etc. Optimizing these issues means the app is still up and running, though traffic and data demand intensify.
- Automation and scaling: Automated systems are one of the most significant players in SaaS scalability. Traffic spikes become effective storms for AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure for allocating resources automatically without crashing or slowing down operations. Continuous monitoring and careful configuration are very important in making resource usage efficient while not overspending.
- Security and compliance monitoring: There is no exception to the generalization; security risks multiply with the application. Regular monitoring cycles of the encryption protocols, user authentication systems, and compliance standards can be a strong remedy to cyber threat survival and regulatory compliance. Security maintenance should be holistic in timely patching, anomaly detection, and routine vulnerability assessments.
- Healthy and optimized database: Databases are the backbone of applications of SaaS, and thus, their performance has a direct effect on the application’s scalability. With increased data, the queries for databases are slower and consume more resources. Regular maintenance, like indexing, query optimization, and data pruning, ensures smooth performance.
- User experience monitoring. It is important to monitor how people use the application, since it will provide more insights into the application performance than just being technical. Monitoring user behavior will expose the pain points, which might not be easily understood from a technical point of view. Continual review and updates based on user feedback keep the application pertinent to the new audience.
- Capacity Needs for Future Planning: Monitoring and maintenance also cover strategic capacity planning. Based on historical analyses of data and utilization trends, traffic patterns, and resource consumption, it is very much possible to predict when additional resources will be needed, thus allowing businesses to scale proactively instead of reactively without interruptions.
Trends in SaaS Scalability: Getting Ready for the Future
Scalability has continued to remain one of the top priorities of SaaS. As the new trend continues to evolve, emerging technologies continue to reshape scalability, allowing SaaS applications to grow more easily, efficiently, and effectively in their performance and security. Trends include the following:
- Predictive scalability with AI and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML allow SaaS platforms to prepare for demand and adjust resources automatically in real-time, minimizing manual intervention and optimizing scalability.
- Serverless computing: Serverless architecture doesn’t require managing servers, allowing apps to automatically scale depending on fluctuating traffic patterns.
- Edge computing: Edge computing shortens latency by processing data close to the user, resulting in faster response times and improved user experience across the globe.
- Microservices architectures: Decomposing applications into smaller, independently scalable services makes them more flexible and speeds up development cycles.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud environments: Scalability, redundancy, and availability are enhanced by having multiple clouds and hybrid, on-premise infrastructures.
- Enhanced security and compliance at scale: As the SaaS application scales, AI-driven security tools and built-in compliance features will aid in safeguarding sensitive data and fulfilling regulatory requirements.
- Sustainability and green cloud computing: Cloud providers are going eco-friendly, and SaaS companies will scale efficiently while saving energy and minimizing their carbon footprint.